Gastroesophageal reflux disease causes heartburn and burning in the chest. Learn about the causes, signs and effective treatments at home or as prescribed by your doctor!
1. What is Gastroesophageal Reflux?
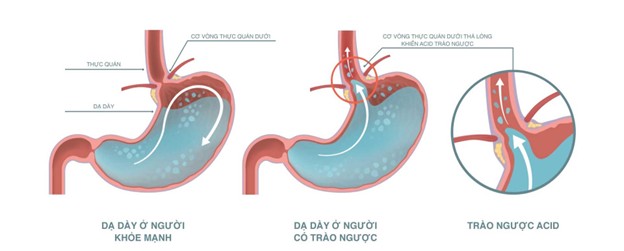
Gastroesophageal reflux is a condition that occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back up into the esophagus (the tube connecting the mouth to the stomach). In healthy individuals, the lower esophageal sphincter closes after food descends into the stomach. If this muscle is weak or abnormally relaxed, acid will rise, causing damage to the esophageal lining, leading to inflammation and uncomfortable symptoms.
5 Causes of reflux that we should know about:
🍟 Unscientific eating habits: Fried food, sour and spicy hot food, late-night eating.
🍷 Drinking alcohol, beer, coffee: Relax the esophageal sphincter.
🚬 Smoking: Increased gastric acid secretion.
🧘 Prolonged stress: Stimulate the stomach to produce acid.
🤰 Pregnancy/Obesity: Abdominal pressure pushes acid up into the esophagus.
2. Signs of Recognizing Gastroesophageal Reflux – How Many Symptoms Are You Experiencing?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease often causes the following symptoms:
- Heartburn, sour burps: Burning sensation from the chest radiating to the neck, increasing when lying down or after eating.
- Acid reflux: Sour/bitter taste in the mouth, burping, acid reflux.
- Epigastric pain: đau above the navel
- Choking, stuck in the throat: Feels like there is a foreign object in the throat.
- Insomnia: Discomfort, coughing at night due to reflux when sleeping.
- Bad breath: Acid reflux causes unpleasant odors.
3. Who is at risk of gastroesophageal reflux? Risk factors to be aware of!
- People who are overweight, obese, and have little physical activity.
- There are unhealthy lifestyles and eating habits such as drinking alcohol and beer, coffee, tea, eating a lot of sour food, consuming a lot of fat, little exercise, lying down immediately after eating…
- Smoking or passive smoking from tobacco smoke
- People work under stress, staying up late incessantly.
- Pregnant women (from the fourth month onwards).
- Hiatal hernia: The upper part of the stomach bulges up through the diaphragm.
- Individuals with a history of illnesses: scleroderma, delayed gastric emptying, etc.
4. When do you need to see a doctor?
- You need to seek medical attention immediately if you experience pain in the upper abdomen, chest pain, especially if accompanied by shortness of breath that could be mistaken for symptoms of cardiovascular disease – this could be a sign of a heart attack.
- There are severe or frequent symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux that affect daily activities.
- Must take medication for gastroesophageal reflux at least twice a week and it doesn't help.
5. Treatment for Gastroesophageal Reflux: Solutions from Experts
5.1. Home treatment, without medication
-
Adjust your diet:
– Limit some foods: spicy food, sour food, hot food, stimulants (tea, coffee, alcohol,…), carbonated drinks, chocolate, mint, garlic,…
– Eat in moderation: Do not eat too full, do not let yourself get too hungry.
– Eat on time: không ăn quá muộn, tránh nằm ngay sau ăn. Bữa ăn cuối ngày nên kết thúc trước khi đi ngủ ít nhất 3 giờ.
– Eat slowly and chew thoroughly: Reduce digestive pressure and avoid swallowing air.
-
Change your lifestyle:
– Raise your head when sleeping: Use a pillow 10-15 cm high or use an anti-reflux pillow to prevent acid reflux at night.
– Sleep on your left side: Keep the stomach lower than the esophagus to reduce reflux.
– Weight loss: Being overweight increases abdominal pressure, making reflux more likely. Regular exercise helps lose weight and sweat. About 30 minutes to 2 hours a day. Exercise at least 5 days a week.
– Quit smoking
– Avoid bending down after eating: Limit exercising or doing heavy work right after a meal.
– Avoid anxiety and stress, avoid staying up late: Practice yoga, meditation, and deep breathing to reduce stress that exacerbates symptoms.
5.2. Drug treatment
- Acid secretion inhibitors: Esomeprazole, Pantoprazole, ... (take 30 minutes before meals).
- Alginate: The formation of an 'alginate raft' layer may help block acid pockets and prevent gastric acid reflux after eating.
- Acid neutralizing drugs: Phosphalugel, Gastropulgite, ....
5.3. Endoscopic or surgical intervention
Gastroesophageal reflux may require endoscopic intervention (such as tightening the esophageal sphincter with LINX silicone rings, injecting substances to thicken the sphincter, using a procedure that creates small scars in the sphincter to help it tighten more, known as the Stretta Procedure, etc.) or surgery (like Nissen fundoplication) if it does not respond to medication or lifestyle changes.
Conclusion:
Whichever method you choose, please combine them. healthy lifestyle and adjustments chế độ ăn to optimize the treatment effectiveness. Don't hesitate. CONTACT DOCTOR If symptoms do not improve! Share the post to help loved ones in the same room!
Reference document
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). MedlinePlus. Updated May 6, 2024. Accessed June 15, 2024. https://medlineplus.gov/gerd.html
#GastroesophagealReflux #GERD #Belching #SourBelch #DigestiveHealth
#StomachPain #BadBreath #Obesity #Pregnancy #Smoking #Stress
#HomeTreatment #HealthyEating #RefluxMedication #EndoscopicSurgery #GERDPrevention