Suddenly one day you see a strange lump appear in your abdomen, groin or navel? That could be a sign of "hernia" – a fairly common condition but should not be taken lightly. This article explains in the simplest, easiest-to-understand way about gastrointestinal hernia, helping you to recognize it early, prevent it properly and know when to seek urgent treatment!
1. What is a Hiatal Hernia?
Hernia occurs when part of an internal organ (such as the intestines or fatty tissue) “bulges” out of its normal position through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or tissue. You may be able to see or feel a bulge, especially when coughing, straining or carrying heavy loads.
👉 Common locations: Groin, navel, old surgical wound
2. 5 Common Types of Gastrointestinal Hernias – Which Type is Dangerous?
Inguinal Hernia (Hernia in the Groin): most popular. Common in men. Part of the intestine or fat passes down into the inguinal canal, causing swelling and pain in the groin area (between the thigh and lower abdomen).
Femoral hernia: Less common, usually in women. The bulge appears near the thigh, below the groin crease.
Umbilical hernia: Occurs right at the navel area. Very common in newborn and pregnant woman or postpartum due to increased abdominal pressure.
Incisional hernia: Occurs at the site of previous surgery. The old incision has weakened the abdominal wall.
Hiatal hernia: The upper part of the stomach “flows” up into the chest through an opening in the diaphragm, which can cause reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus nặng.
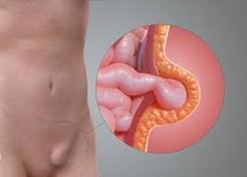
Figure 1: Inguinal hernia
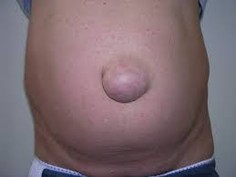 Figure 2: Umbilical hernia
Figure 2: Umbilical hernia
3. Causes of Gastrointestinal Hernia Everyone Should Know!
Hiatal hernia is usually the result of two main factors:
- Weak muscle/tissue:
- Maybe because weak muscle structure from birth
- Old age
- Old surgical wound.
- Sudden or persistent increase in intra-abdominal pressure:
- Coughing a lot, coughing for a long time (smoking, bronchitis).
- Frequent constipation, have to strain.
- Carrying heavy objects in the wrong position or beyond your capacity.
- Pregnant.
- Overweight, obesity.
- Playing sports too hard.
4. Early Warning Signs – Don’t Ignore Them!
- Marked swelling/bulging: This is the most typical sign and is early warning signs
- Appears in the groin, navel, abdominal area with old surgical scars, or near the thighs.
- Gets bigger when you stand up straight, cough, sneeze, or strain.
- Flatten or disappear when you lie down, press lightly.
- Feeling of pressure, heaviness, or stabbing pain: Especially when you exercise vigorously, lift heavy objects, cough, or bend over. This feeling may lessen with rest.
🚨 DANGER signs requiring IMMEDIATE EMERGENCY (Strangulated hernia):
- The bulge is HARD, EXTREMELY PAINFUL, and cannot be pushed up/down.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Bloated stomach, unable to fart or defecate.
- Fever.
If you have these signs, please go to hospital immediately because it can cause intestinal necrosis, life threatening!
5. Dangerous Complications
If left untreated, especially when strangulated hernia, you may encounter:
- Intestinal obstruction: The intestine is blocked and cannot pass food.
- Intestinal necrosis: The trapped part of the intestine is deprived of blood supply, leading to cell death.
This is surgical emergency extremely dangerous
6. Diagnosis & Treatment Solutions
6.1. How does the doctor diagnose?
- Clinical examination: Main! The doctor will ask you to stand, cough, and strain to observe the bulge.
- Abdominal ultrasound or CT scan: Helps to see more clearly the location, size and type of hernia, especially with small or difficult to see masses.
6.2. Main treatment method: SURGERY
- Why surgery? To push the protruding organ back into place and the most important thing is to firmly stitch the weakened/torn muscle/tissue wall., preventing gastrointestinal hernia from recurring.
- Common surgical methods:
- Laparoscopic surgery: The doctor makes several small incisions and uses a camera and specialized tools to make the repair. Less pain, faster recovery, good aesthetics.
- Open surgery: Make a larger incision directly at the hernia site. Still effective, especially for complex cases.
- After surgery: Usually quick, you can go home after a few days if nothing unusual. You need to follow the doctor's instructions for movement and wound care.
- Is surgery always necessary?
- With strangulated hernia: Emergency surgery is required.
- With common hernias that cause pain, discomfort, and affect daily activities: Early surgery is recommended.
- With small, asymptomatic hernias: continued monitoring may be possible.
7. Prevention Tips From Experts

- Maintain a healthy weight: Avoid being overweight or obese as this puts a lot of pressure on the abdomen.
- Eat foods rich in fiber: Prevent constipation (green vegetables, fruits, whole grains). Drink enough water.
- Lifting heavy objects the RIGHT WAY:
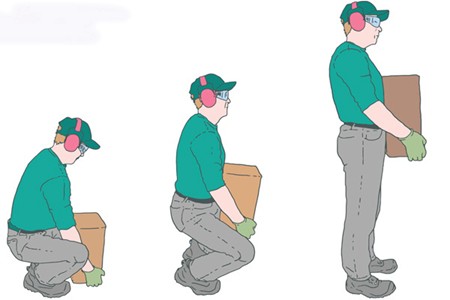
- Abdominal muscles, keep your back straight
- Use force from the legs, do not bend over to lift objects.
- Don't try too hard! Ask for help or use a cart.
- Quit smoking: Relieves chronic cough – a cause of abdominal pressure.
- Exercise regularly: Focus on exercises that strengthen your abdominal and pelvic floor muscles (like Kegel exercises), but need to practice technically correct to avoid harm. Avoid strenuous movements that suddenly increase abdominal pressure.
- Completely cure diseases that cause cough, sneezing, and prolonged constipation.
8. When Should I See a Doctor Immediately?
➡️ Please Make an appointment during the week immediately if:
- Detect any unusual lumps or swellings any abdominal, groin, navel or previous surgical site.
- Feel pain, discomfort, discomfort persistent in these areas, especially with exercise.
🚑 GO TO THE EMERGENCY HOSPITAL IMMEDIATELY If you have signs of strangulated hernia:
- The mass is very painful, swollen, red, hard, and cannot be pushed up/down.
- Nausea, vomiting a lot.
- Severe abdominal pain, abdominal distension.
- Unable to poop or fart.
- Fever.
Hernias do not heal on their own, but they can be completely treated and effectively prevented! Understanding the disease helps you proactively protect your health. Do not hesitate to see a doctor immediately when there are suspicious signs, early treatment is always much simpler and safer.
References
- National Library of Medicine. Hernia. MedlinePlus. Updated July 1, 2021. Accessed June 7, 2025. https://medlineplus.gov/hernia.html
#hernia #hernia surgery #laparoscopic surgery #open surgery #strangulated hernia #surgical emergency #intestinal obstruction #intestinal necrosis #hernia treatment #hernia diagnosis #hernia signs #abdominal bulge #inguinal hernia #umbilical hernia #lower abdominal pain #hernia warning #hernia danger
